Fokker
Fokker G.1 WW2 Fighter
|
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.
History Fokker Aerospace
Fokker G.1 WW2 Fighter
First flight 16 March 1937 Number built 63

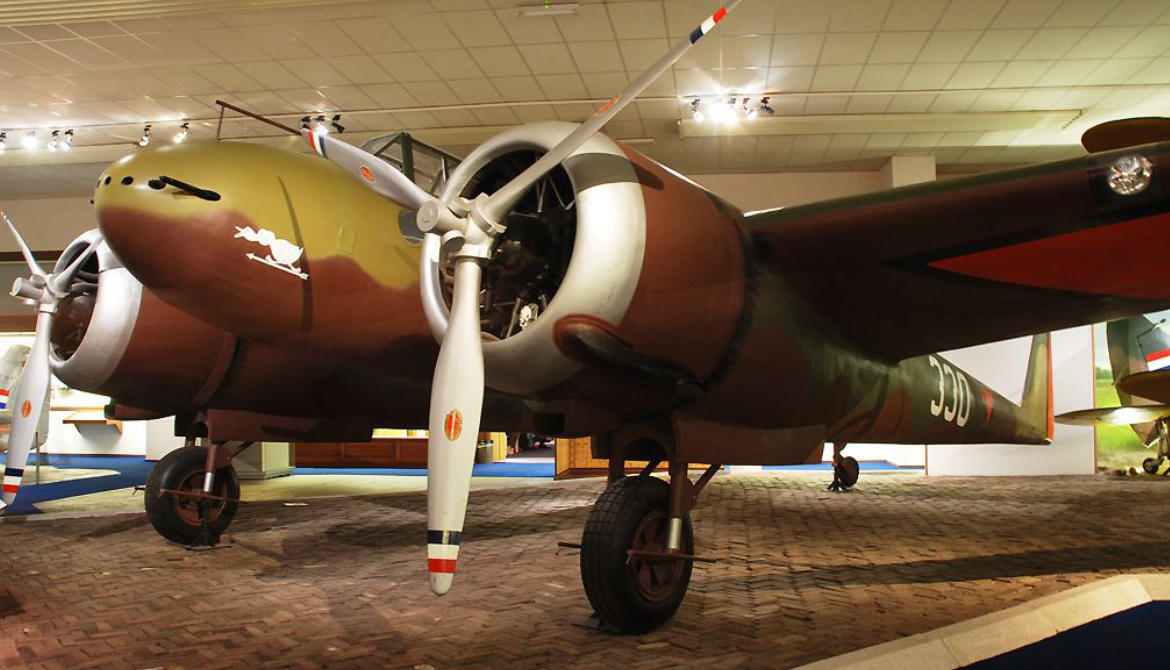
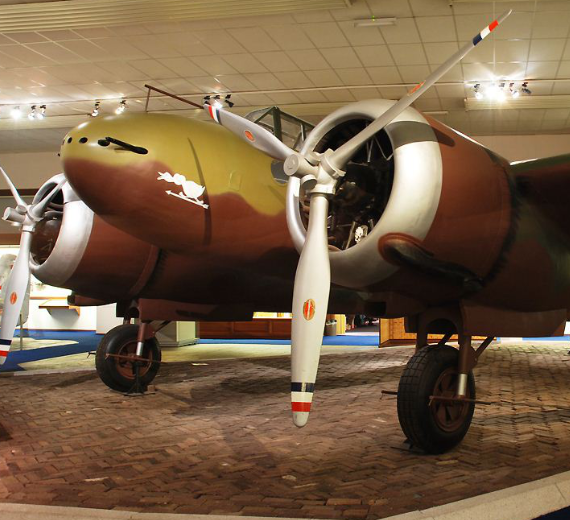
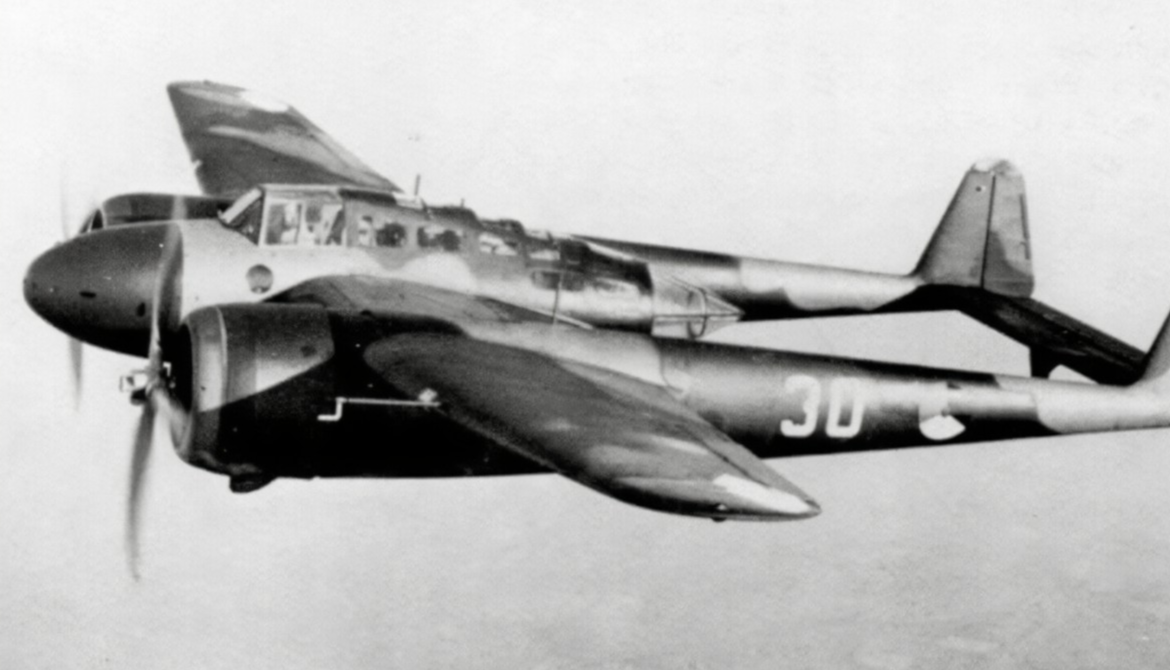
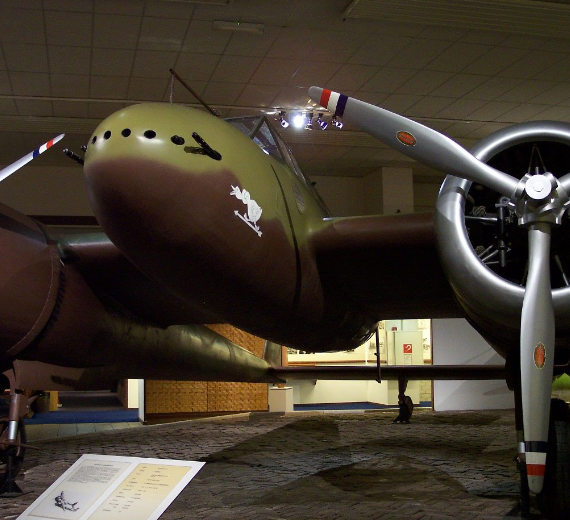
The Fokker G.I was a Dutch twin-engined heavy fighter aircraft comparable in size and role to the German Messerschmitt Bf 110. Although in production prior to World War II, its combat introduction came at a time the Netherlands were overrun by the Germans. The few G.Is that were mustered into service were able to score several victories. Some were captured intact after the Germans had occupied the Netherlands. The remainder of the production run was taken over by the Luftwaffe for use as trainers.
Design and development

Duration: 1 minute and 55 seconds.1:55
The G.I, given the nickname le Faucheur ("The Reaper" in French), was designed as a private venture in 1936 by Fokker chief engineer Dr. Schatzki. Intended for the role of jachtkruiser, "heavy" fighter or air cruiser, able to gain air superiority over the battlefield as well as being a bomber destroyer, the G.1 would fulfill a role seen as important at the time, by advocates of Giulio Douhet's theories on air power. The Fokker G.I utilized a twin-engined, twin-boom layout that featured a central nacelle housing two or three crew members (a pilot, radio operator/navigator/rear gunner or a bombardier) as well as a formidable armament of twin 23 mm (.91 in) Madsen cannon and a pair of 7.9 mm (.31 in) machine guns (later eight machine guns) in the nose and one in a rear turret
Operational_history


0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Fokker Aerospace
Fokker G.1 WW2 Fighter


Fokker Aerospace
Fokker G.1 WW2 Fighter
General Info
-
-
- Crew: 2-3
- Length: 10.87 m (35 ft 8 in)
- Wingspan: 17.16 m (56 ft 4 in)
- Height: 3.8 m (12 ft 6 in)
- Wing area: 38.3 m2 (412 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 3,325 kg (7,330 lb)
- Gross weight: 4,800 kg (
Max takeoff weight: 5,000 kg
-
Powerplant
- Fuel capacity: 1,050 L (277 US gal; 231 imp gal)
- Powerplant: 2 × Bristol Mercury VIII 9-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engines, 540 kW (730 hp) each at 2,650 rpm - takeoff power
-
-
-
- 830 hp (620 kW) at 4,100 m (13,500 ft) at 2,750 rpm - maximum continuous power
-
-
-
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 475 km/h (295 mph, 256 kn) at 4,100 m (13,500 ft)
- Range: 1,510 km (940 mi, 820 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 10,000 m (33,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 13.5 m/s (2,660 ft/min) 5,000 m (16,000 ft) in 6 minutes 20 seconds
Armament
- 8× 7.9 mm (0.31 in) forward-firing FN-Browning machine guns in the nose
- 1× 7.9 mm (0.31 in) machine gun in rear turret
- 300 kg (660 lb) of bombs (G.1 Wasp could take 400 kg (880 lb))
Links to Youtube & Others
At the conclusion of hostilities, several G.Is were captured by the Germans, with the remainder of the Spanish order completed at the Fokker plant by mid-1941 in order for the G.1s to be assigned as fighter trainers for Bf 110 crews at Wiener Neustadt.[10] For the next two years, Flugzeugführerschule (B) 8 flew the G.1 Wasp until attrition grounded the fleet
Fokker
Fokker G.1 WW2 Fighter
The Luchtvaartafdeeling ordered 36 G.I's with 541 kW (825 hp) Bristol Mercury VIII engines, the standard engine used by the Dutch Air Force.
Youtube Link
On 10 May 1940, when Nazi Germany invaded the Netherlands, 23 G.1 aircraft were serviceable while production of Spain's order of the G.1 Wasp variant continued with a dozen aircraft completed, awaiting armament.