Russian Aircraft "Mig"
MiG-31 Foxhound
 |
|
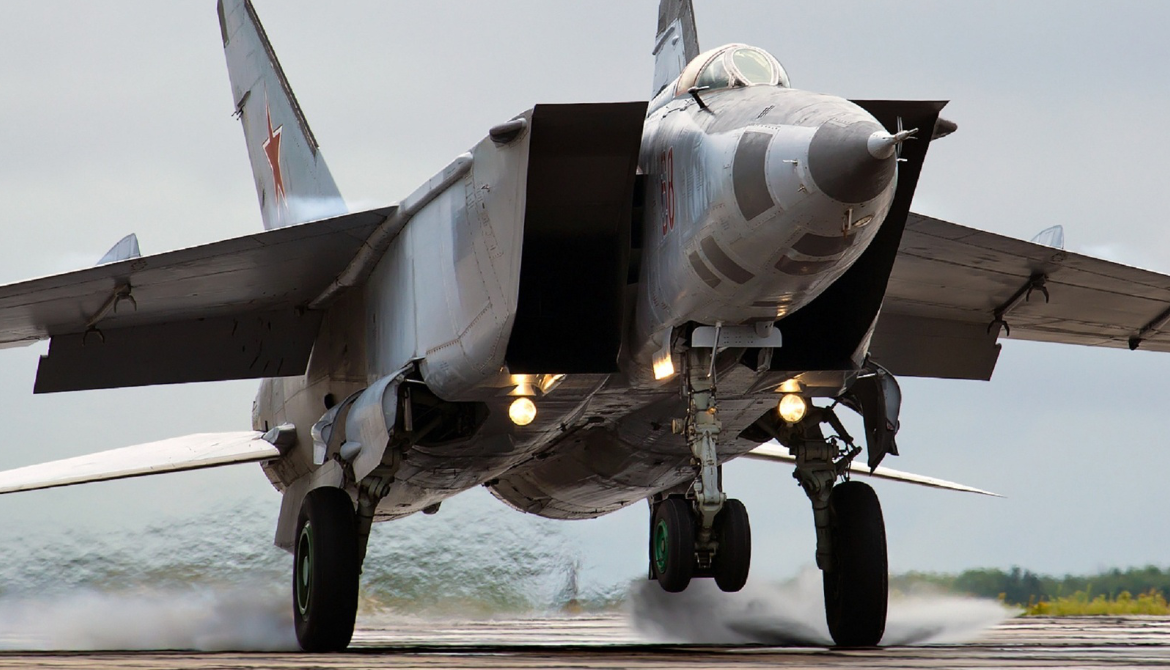
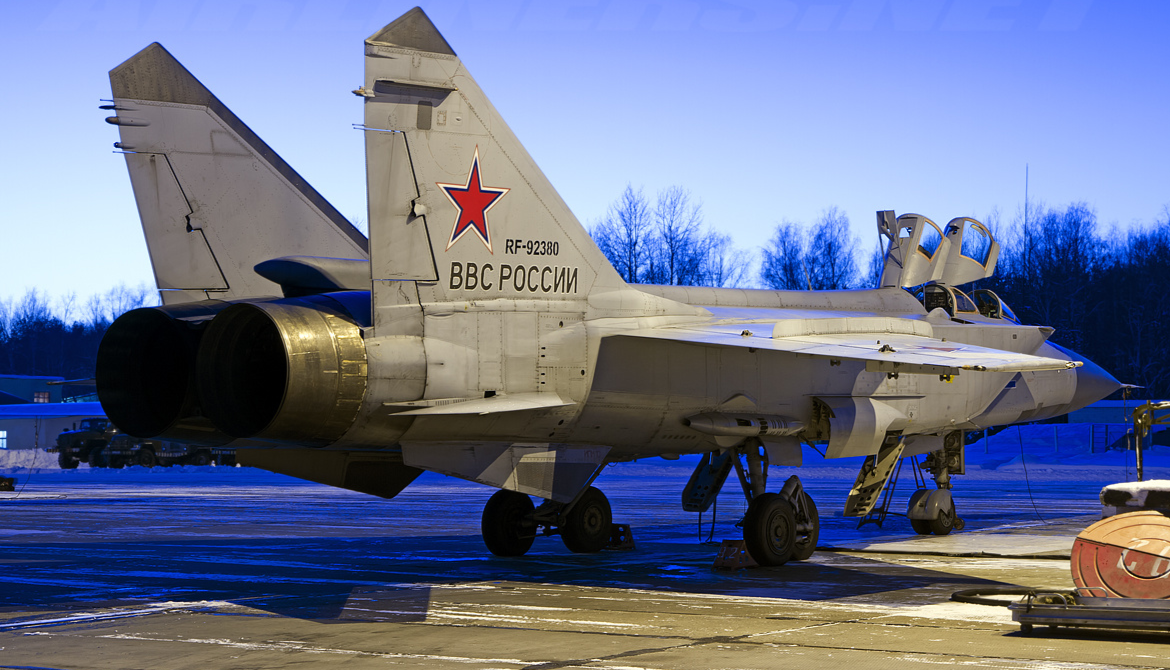
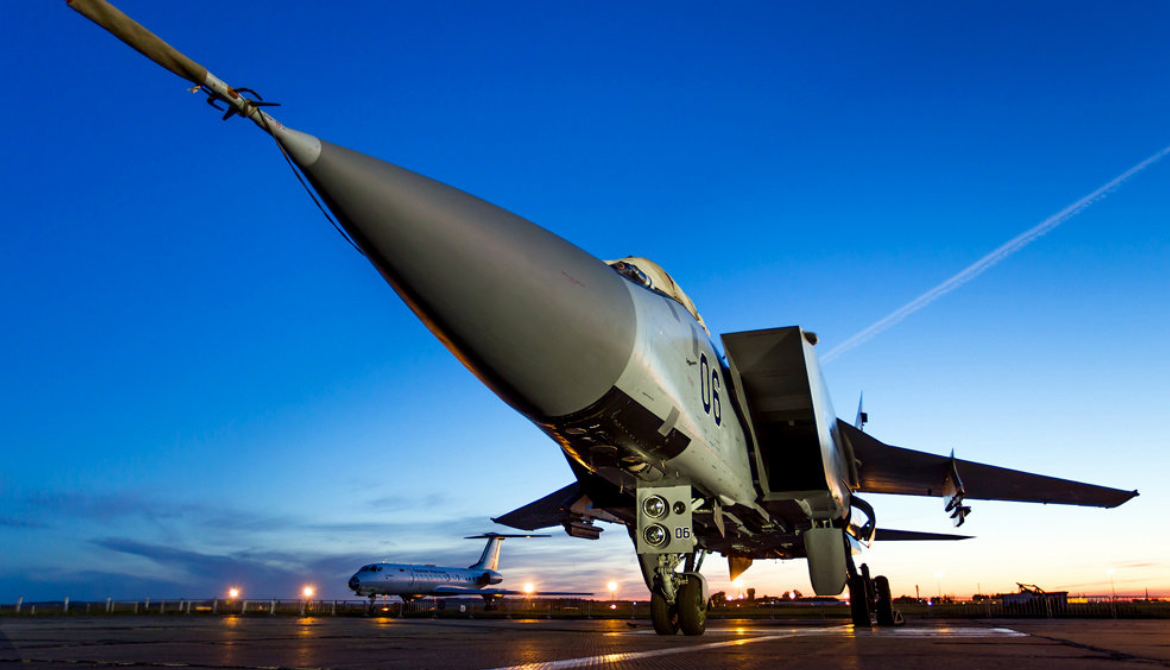
| A Russian Air Force MiG-31DZ in flight over Russia | |
| Role | Interceptor aircraft, attack aircraft |
|---|---|
| National origin | Soviet Union |
| Manufacturer | Mikoyan-Gurevich/Mikoyan |
| First flight | 16 September 1975; 48 years ago |
| Introduction | 6 May 1981 |
| Retired | 2023 (Kazakh Air Force) |
| Status | In service with the Russian Air Force |
| Primary users | Russian Aerospace Forces Kazakh Air Force (historical) |
| Produced | 1975–1994 |
| Number built | 519 |
| Developed from | Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25 |
|
|
.
History Russian Aircraft Corporation "Mig"
Mikoyan MiG-31 NATO reporting name: Foxhound

The Mikoyan MiG-31 (Russian: Микоян МиГ-31; NATO reporting name: Foxhound) is a supersonic interceptor aircraft developed for the Soviet Air Forces by the Mikoyan design bureau as a replacement for the earlier MiG-25 "Foxbat"; the MiG-31 is based on and shares design elements with the MiG-25. The MiG-31 is cited as the third fastest known operational combat aircraft in the world as of the 2020s. It continues to be operated by the Russian Aerospace Forces following the end of the Cold War and the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. The other operator, the Kazakh Air Defense Forces, retired the type in 2023. The Russian Defence Ministry expects the MiG-31 to remain in service until at least 2030; that was confirmed in 2020 when an announcement was made to extend the service lifetime of the existing airframes from 2,500 to 3,500 hours
Design

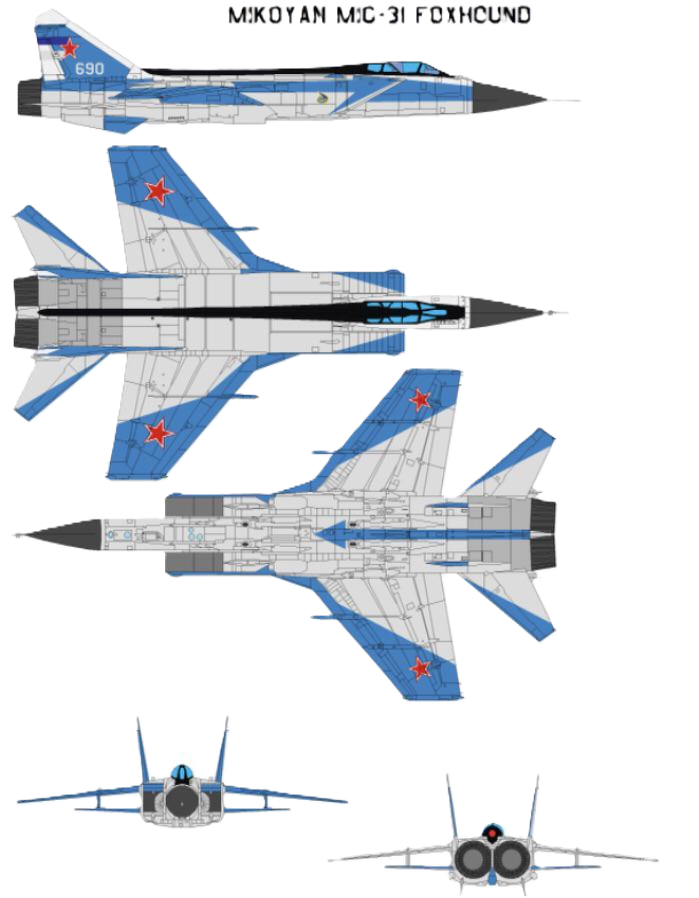
Like the MiG-25, the MiG-31 is a large twin-engine aircraft with side-mounted air intake ramps, a shoulder-mounted wing with an aspect ratio of 2.94, and twin vertical tailfins. Unlike the MiG-25, it has two seats, with the rear occupied by a dedicated weapon systems officer.
The MiG-31 was designed to fulfill the following mission objectives:
- Intercept cruise missiles and their launch aircraft by reaching missile launch range in the shortest possible time after departing the loiter area;
- Detect and destroy low flying cruise missiles, UAVs and helicopters;
- Long range escort of strategic bombers;
- Provide strategic air defense in areas not covered by ground-based air defense systems.
The MiG-31 is limited to five g when travelling at supersonic speeds. While flying under combat weight, its wing loading is marginal and its thrust-to-weight ratio is favorable. The MiG-31 is not designed for close combat or rapid turning

0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
MachAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Russian Aircraft Corporation "Mig"
Mikoyan MiG-31 NATO reporting name: Foxhound


Russian Aircraft Corporation "Mig"
Mikoyan MiG-31 NATO reporting name: Foxhound
General Info
-
-
-
-
- Crew: 2 (pilot and weapons systems officer)
- Length: 22.62 m (74 ft 3 in)
- Wingspan: 13.456 m (44 ft 2 in)
- Height: 6.456 m (21 ft 2 in)
- Wing area: 61.6 m2 (663 sq ft)
-
-
-
Powerplant
-
-
-
- Powerplant: 2 × Soloviev D-30F6 afterburning turbofan engines, 93 kN (21,000 lbf) thrust each dry, 152 kN (34,000 lbf) with afterburner
-
-
-
Performance
-
- Maximum speed: 3,000 km/h (1,900 mph, 1,600 kn) / Mach 2.83 at 21,500 m (70,500 ft)
-
-
-
- 1,500 km/h (930 mph; 810 kn) / Mach 1.21 at low altitude
-
-
- Cruise speed: 2,500 km/h (1,600 mph, 1,300 kn) / Mach 2.35
- Range: 3,000 km (1,900 mi, 1,600 nmi) with 4 × R-33E and 2 drop tanks
-
-
- Combat range: 1,450 km (900 mi, 780 nmi) at Mach 0.8 and 10,000 m
-
-
- Service ceiling: 25,000 m
Armament
- Guns: 1 × 23 mm Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-6-23M rotary cannon with up to 800 rounds (later removed)
- Hardpoints: 4 × semi-recessed under the fuselage and 4 × underwing pylons with capacity of up to 9,000 kg (20,000 lb) of ordnance[
Links to Youtube & Others
The Mikoyan MiG-31 (Russian: Микоян МиГ-31; NATO reporting name: Foxhound) is a supersonic interceptor aircraft developed for the Soviet Air Forces by the Mikoyan design bureau as a replacement for the earlier MiG-25 "Foxbat"; the MiG-31 is based on and shares design elements with the MiG-25.
Russian Aircraft Mig
MiG-31 Foxhound
The cockpit features a conventional centre stick and left hand throttle controls. The pilot sits in a Zvezda K-36DM ejection seat.
Youtube Link
The baseline MiG-29 9.12 has a Phazotron RLPK-29 radar fire control system which includes the N019 Sapfir 29 look-down/shoot-down coherent pulse-Doppler radar and the Ts100.02-02 digital computer.