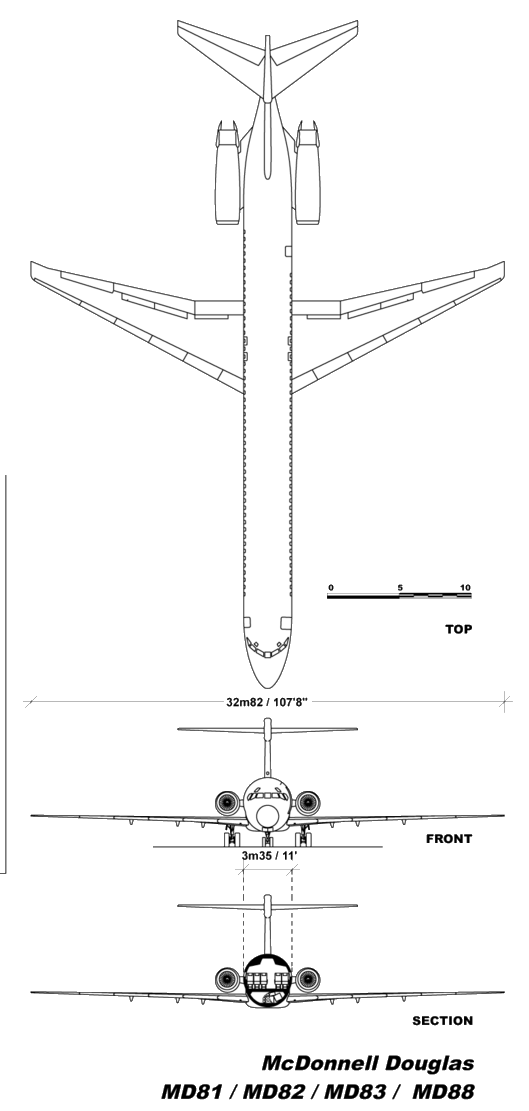
McDonnell/Douglas
MD-80/83 Narrow-body
Role Narrow-body jet airliner
National origin United StatesManufacturer McDonnell Douglas
Boeing Commercial Airplanes (from Aug. 1997)
First flight October 18, 1979
Introduction October 10, 1980, with Swissair
Status In service; mostly for cargo transport
Primary users Aeronaves TSM
World Atlantic Airlines
LASER Airlines
Everts Air
Produced 1979–1999
Number built 1,191
Developed from McDonnell Douglas DC-9
Developed into McDonnell Douglas MD-90 / Boeing 717
Comac ARJ21
.
History McDonnell/Douglas
McDonnell Douglas MD-80/83 First Flight October 18, 1979
Produced 1979–1999

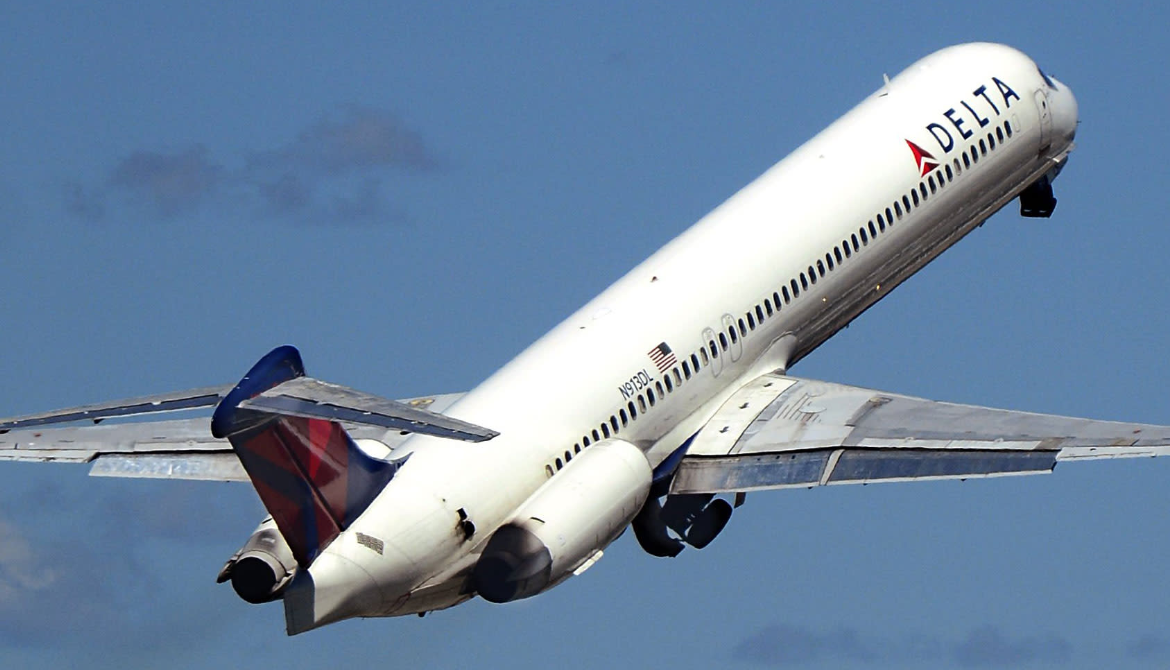
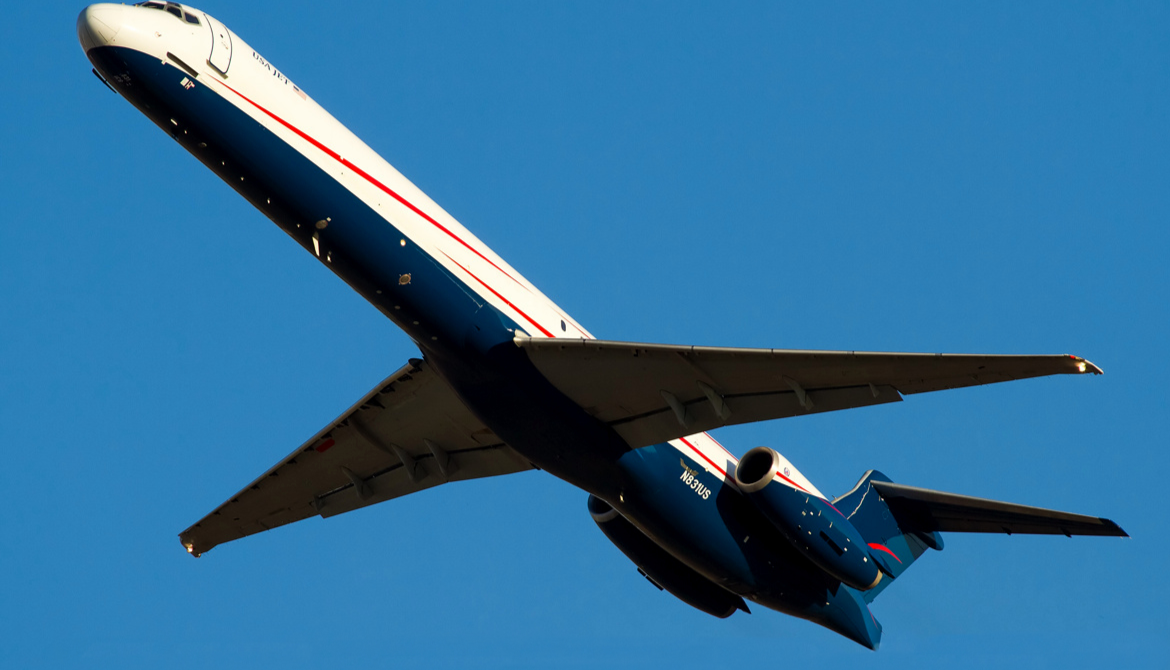
The McDonnell Douglas MD-80 is a series of five-abreast single-aisle airliners developed by McDonnell Douglas. It was produced by the developer company until August 1997 and then by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. The MD-80 was the second generation of the DC-9 family, originally designated as the DC-9-80 (DC-9 Series 80) and later stylized as the DC-9 Super 80 (short Super 80). Stretched, enlarged wing and powered by higher bypass Pratt & Whitney JT8D-200 engines, the aircraft program was launched in October 1977.
The DC-9 series, the first generation of the DC-9 family, entered service in late 1965 and became a commercial success with 976 units built when production ended in 1982.[2] The all-new designed aircraft family includes five members or variants (DC-9-10 / DC-9 Series 10, Series 20, Series 30, Series 40, and Series 50) with ten sub-variants or versions (Series 11, Series 12, Series 14, Series 15, Series 21, Series 31, Series 32, Series 33, Series 34, Series 41, and Series 51) and features two rear fuselage-mounted turbofan engines, a T-tail configuration,[3] a narrow-body fuselage with five-abreast seating for 80 to 135 passengers.[4] The success prompted the manufacturer to further develop the aircraft family with the last member, Series 50, as the reference aircraft..
Variants
Type certification (TC)

Following the MD-81's first flight on October 18, 1979, the MD-82 and MD-83 made their maiden flights on January 8, 1981, and December 17, 1984, respectively They were then certified by the FAA on August 25, 1980, July 29, 1981, and October 17, 1985, respectively. The first airliner, an MD-81, was delivered to launch operator Swissair on September 13, 1980 Instead of merely using the MD- prefix as a marketing symbol, an application was made to again amend the type certificate to include the MD-81, MD-82, and MD-83. This change was dated March 10, 1986, and the type certificate declared that although the MD designator could be used in parentheses, it must be accompanied by the official designation, for example: DC-9-81 (MD-81). All Long Beach aircraft in the MD-80 series thereafter had MD-81, MD-82, or MD-83 stamped on the aircraft nameplate


The MD-87 and MD-88 made their first flight on December 4, 1986, and August 15, 1987, respectively.Although not certified until October 21, 1987, McDonnell Douglas had already applied for models DC-9-87 and DC-9-87F on February 14, 1985. The third derivative was similarly officially designated DC-9-87 (MD-87), although no nameplates were stamped DC-9-87. For the MD-88, an application for a type certificate model amendment was made after the earlier changes, so there was not a DC-9-88, which was certified on December 8, 1987 The FAA's online aircraft registry database shows the DC-9-88 and DC-9-80 designations in existence but unused
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
McDonnell/Douglas
McDonnell Douglas MD-80/83 First Flight October 18, 1979
Produced 1979–1999


McDonnell/Douglas
McDonnell Douglas MD-80 First Flight October 18, 1979
Produced 1979–1999
General Info
Performance
Related development
Links to Youtube & Others
The F101 was developed specifically for the Advanced Manned Strategic Aircraft, which became the B-1A. The F101 powered the four development aircraft from 1970 to 1981.
McDonnell/Douglas
MD-80 Narrow body
The McDonnell F-101 / RF-101 Voodoo was initially designed as a long-range bomber escort, but had its role adjusted to a nuclear-armed fighter-bomber and a photo reconnaissance aircraft
Youtube Link
The General Electric F101 is an afterburning turbofan jet engine. It powers the Rockwell B-1 Lancer strategic bomber fleet of the USAF.